Table Of Content
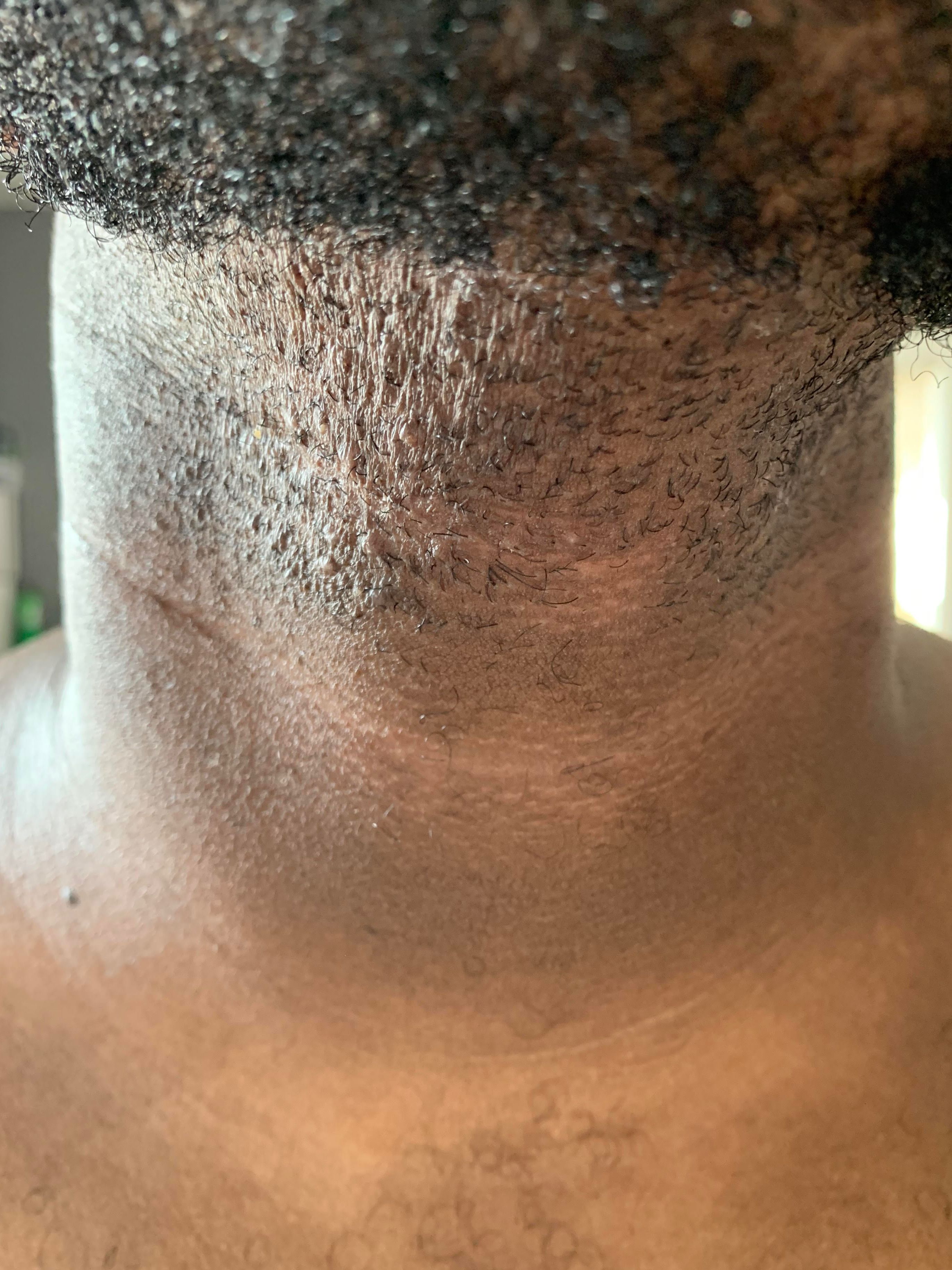
The ingrown hair may eventually make its way out of your skin. There are also situations where the hair will continue growing under your skin. In this case, Dr. Bullard suggests seeing a dermatologist. Dermatologist Sherrie Bullard, MD, shares safe ways to get rid of ingrown hairs and how to prevent them from happening. There will be a painful bump and swelling, and you may notice pus. If bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens enter the skin, an infection can develop, known as folliculitis.
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider?
If you look closely, you may be able to see the ingrown hair loop around and re-enter the skin. Seek medical attention if you observe or suspect any of these symptoms. An infected ingrown hair can potentially lead to complications if left untreated. This removes a dead layer of skin cells and helps release ingrown hairs. Make small, circular motions to wash the affected areas with a washcloth, exfoliating brush, exfoliating gel, or scrub. If you shave, tweeze, or wax your hair, you can develop ingrown hairs.
Medications
About 30% of people also have this bacterium living in their nose, although it may not cause symptoms. While cases of staph are becoming rarer in hospitals, they may be increasing in the wider community. Still, it is important to note that the likelihood of acquiring sepsis from ingrown hair is highly unlikely.
5 Belly Button Infections You Can Get (and What to Do If You Have One) SELF - Self
5 Belly Button Infections You Can Get (and What to Do If You Have One) SELF.
Posted: Sat, 23 Feb 2019 08:00:00 GMT [source]
More on Skin Problems and Treatments
An ingrown hair can lead to a localized foreign-body inflammatory reaction, which causes pinpoint red or pink bumps on the skin. Hair structure and direction of growth play a role in ingrown hair. A curved hair follicle, which produces tightly curled hair, is believed to encourage the hair to reenter the skin once the hair is cut and starts to grow back.
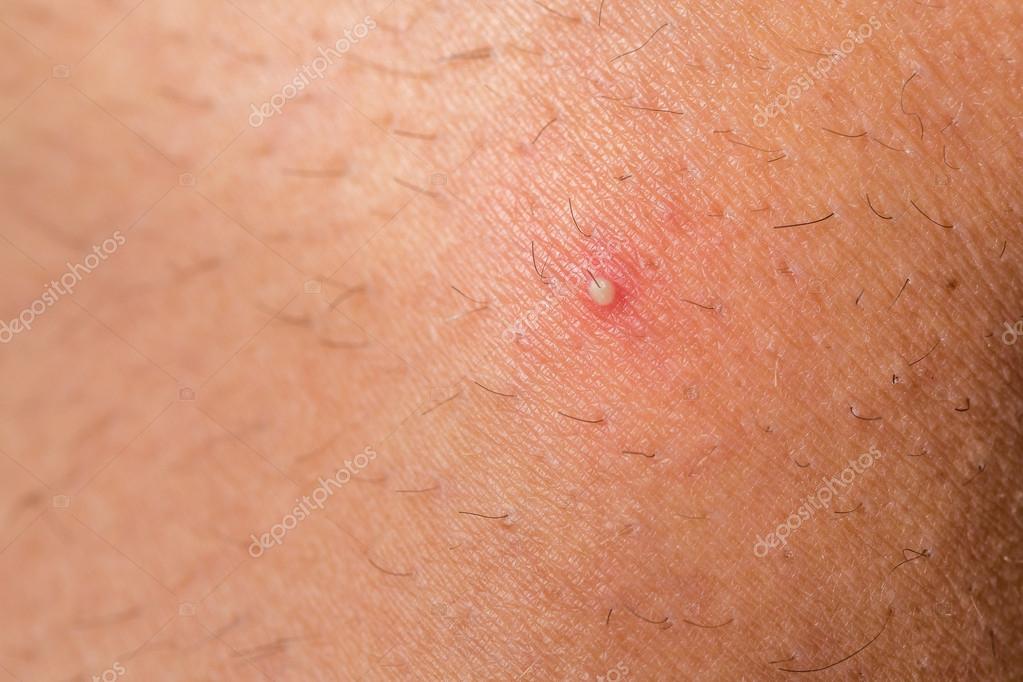
Preventing ingrown hair infections involves adopting a careful approach to hair removal and skincare routines. It's not common, but you can develop a staph infection from ingrown hairs if they're not treated. Symptoms include a pimple at your ingrown hair's follicle, warmth or swelling around your ingrown hair, fever, or a general feeling of illness. If you see signs of infection, contact your doctor. Infections can develop around the ingrown hair, causing pus formation, discoloration and pain, though.
How do you get rid of an ingrown hair cyst?
It’s believed that razors with at least two edges can also lead to transfollicular penetration. As the first blade pulls the hair up, the next blades cut the hair in a way that causes the hair to go back into the skin after shaving. If you notice one or more of these symptoms, see a physician or health professional for help as soon as possible. What if you’ve tried home remedies, and the ingrown hair just won’t go away?
If an ingrown hair becomes infected, you may notice the bumps getting bigger and more painful. Pustules occur when there’s pus around the follicles. An ingrown hair looks like a raised, discolored spot on your skin.
How do I get rid of a cyst in my pubic area?
If infections recur or are severe, you may need medical treatment. Staph infections can spread to the bloodstream and become very serious. They do not go away on their own, so it is crucial to seek medical attention quickly to receive prompt treatment. Staphylococcus is the name for a group of over 30 different types of bacteria. One type of staph that lives naturally on human skin is Staphylococcus aureus.
Drugs & Supplements
Infected ingrown hairs can vary in severity and appearance. They can lead to increased inflammation, pain, and the formation of pustules or cysts. If the hair is completely under your skin, avoid the temptation to poke the area with a sharp object and dig out the hair. Please see a healthcare professional for help in this situation. Your health care provider is likely to diagnose ingrown hair by looking at your skin and asking about your hair removal habits.
Hyperpigmentation can last for several months or longer after the ingrown hair has improved. If you notice some darker patches of skin, you can apply a topical retinoid which may improve the hyperpigmentation. An ingrown hair occurs when a hair that has been shaved, waxed, or plucked begins to grow back into the skin. In the days before your medical appointment, if possible, stop shaving or using any form of hair removal. Ingrown hair may worsen at first as the hair grows back. Most ingrown hairs will go away on their own without treatment after a few days; though, severe cases may take several weeks.
It’s not a good idea to pop or squeeze an ingrown hair cyst, as you can introduce bacteria that can cause an infection. If the bumps or cysts become extremely bothersome — or if they aren’t fading — see a healthcare professional or dermatologist. Although no cure exists, it is possible to decrease the occurrence of ingrown hairs. The easiest way to do this is through proper hair and skin hygiene. Ingrown hairs can have a few potential complications. The most common complication is lasting hyperpigmentation after the inflammation has gone down.
So it’s important to follow a doctor or healthcare professional’s directions. Antibacterial washes, such as benzoyl peroxide (Clearasil, Proactiv) or chlorhexidine (Hibiclens), can be used once or twice a day to control the infection. Hence, it can be useful as long-term therapy in individuals with excessive facial hair or patients who have pseudofolliculitis barbae. Make sure you are shaving in the direction the hair is growing. Shaving against the grain can increase your chance of developing an ingrown hair since this can cause the sharp tip of the hair to retract into the skin.
Applying shaving cream five to 10 minutes before shaving can make the hair softer. This may reduce the sharp hair tips that can become embedded as ingrown hairs. Applying a warm compress prior to shaving can provide these benefits as well. The most effective way to prevent ingrown hairs is to stop shaving.
Ingrown hair cysts often show up where your hair is coarse or curly, like in the pubic region. You might be more likely to get ingrown hair cysts if you have coarse or curly hair. The cysts can also form where dead skin cells are blocking hair follicles. If ingrown hairs continue to form, see a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying causes. They may also recommend more permanent hair removal methods, such as laser hair removal, to help reduce your risk of ingrown hairs and bumps.
Whatever the reason may be for wanting or needing to shave, there are other ways to prevent ingrown hairs. Symptoms can start roughly one to two days after you shave or wax. An ingrown hair may look like a small, swollen, raised bump that is the same color as your skin, red, or hyperpigmented (has patches of dark spots).